
P0300 is a generic OBDII code that can occur with the Pontiac Firebird. This code indicates that your car’s engine is misfiring and can be a drivability threat.
P0300 is often accompanied by cylinder-specific misfire codes (P030X, where the X indicates the cylinder number that is misfiring). If you have P0300 and a cylinder-specific misfire, the cylinder indicated by the specific codes would be where to start looking for your problem.
Worn spark plugs, coil packs, or plug wires are the most common cause of P0300.
Table of Contents
| Definition | P0300: Random Multiple Misfire Detected. |
| Symptoms | Rough idle, jerks when accelerating, decreased MPG. |
| Common Causes | Ignition components or it’s a symptom of another problem. |
| Breakdown Risk? | Yes. |
| Repair Cost (Parts) | Typically less than $250 for the common issues. |
| Repair Difficulty | Easy, if it’s ignition related. |
Pontiac Firebird P0300 Meaning

P0300 is a general diagnostic trouble code. Specifically, it indicates that there is a:
Random, Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
P0300 is a random misfire code, which means that it is not going to tell you which cylinder is causing the misfire.
Since something is causing cylinders to misfire randomly, figuring out the cause is less cut and dry than a cylinder-specific misfire code. This code can indicate an issue with the ignition system, but it is often a symptom of another problem.
How you approach P0300 depends on if there were any other codes present.
P0300 Symptoms: Pontiac Firebird
There are almost always noticeable symptoms associated with P0300 other than the check engine light.
- Check engine light (it may be flashing, which indicates you should stop driving your car ASAP).
- Your car will likely have a noticeable misfire sound to it.
- Your Firebird will jerk while accelerating.
- Excess vibration, especially at lower RPM.
- Decreased fuel economy.
If your Firebird’s engine is misfiring enough to damage the catalytic converter, the check engine light may flash on and off as a warning to stop running the engine until you can fix it.
P0300 Trouble Code Causes + Diagnosis

When diagnosing the cause of P0300 in your Pontiac Firebird the problem can be broken down into two main categories.
- Something related to the ignition system caused the random misfire.
- P0300 is a symptom of another engine problem.
Important to pull and weigh all the codes together. The misfiring could just be a symptom of the real problem.
For example, if you got a fuel pressure-related code, that indicates your Firebird’s fuel rail isn’t getting enough fuel pressure for the fuel injectors to work properly, which would cause a random misfire.
Spark Plugs, Plug Wires, or Coil Packs (Ignition)
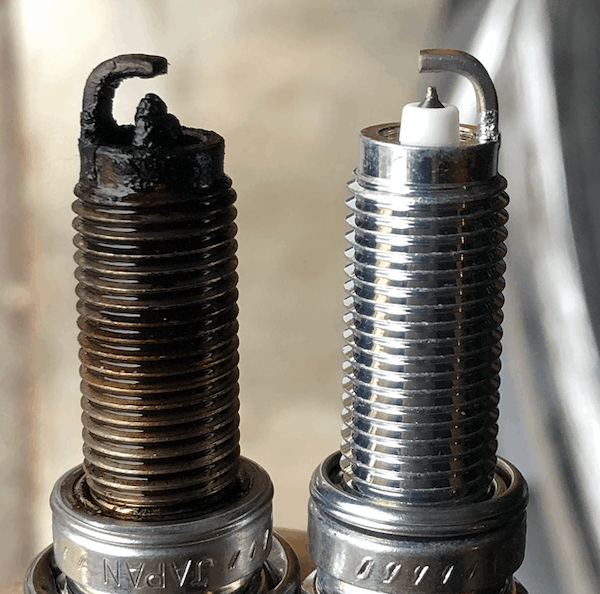
Start here if your Firebird has only misfire/ignition-related codes.
The most likely cause of P0300 in most vehicles is a bad ignition component (particularly the spark plugs).
While most modern vehicles use iridium spark plugs that can last a long time, they still should be changed at Pontiac’s recommended maintenance intervals.
If your Firebird has a few cylinder-specific trouble codes, it may be a good idea to check and see if there is any wiring damage around the wiring harness connecting the PCM to the coil packs.
Here’s how to test a coil pack, how to tell if a spark plug is bad (video), and how to test plug wires (video).
Low Fuel Pressure

If your Firebird’s fuel pressure is low, you may also encounter P0171 (fuel trim lean) or P0087 (fuel rail pressure too low).
If there isn’t enough fuel getting to the engine, it will keep leaning out the air-fuel mixture.
If your car’s fuel pressure is really low, it’ll cause noticeable misfiring as there won’t be enough fuel pressure to atomize the gasoline as it enters the combustion chamber.
Typically, if your Firebird has low fuel pressure, it’ll act fine when it doesn’t need a lot of fuel. But it’ll sputter and act like it will die at speed or under heavy acceleration.
As the fuel pressure decreases, it’ll start happening when you give it less and less gas. Or, your Firebird will shut down when driving but then turn back on.
It’s really easy to check the fuel pressure at the rail. Autozone or any other parts store will usually have a loaner fuel pressure testing kit.
The two most prevalent causes of low fuel pressure are an issue with the fuel pump or fuel regulation.
Here’s some information on how to tell if you have a bad fuel filter. Here’s how to test fuel pressure with a fuel pressure tester.
Vacuum Leak
P0171 is the most common code to see with a vacuum leak
If your Firebird has a vacuum leak, unmetered air is entering the combustion chamber, which usually leans out the air-fuel mixture.
A lean air/fuel ratio will cause the cylinders to misfire, and it’ll throw the P0300.
Since a vacuum leak almost always affects each cylinder the same, you’ll typically get P0300 with it and not any cylinder-specific misfire codes.
Here’s a great article from Popular Mechanics on how to detect a vacuum leak. Chasing one down is pretty easy. Popular Mechanics: How to find a vacuum leak.
Mechanical

Most mechanical issues won’t throw other codes.
Mechanical issues can cause misfiring. Here are the most common mechanical issues that can cause P0300:
- Blown or leaking head gasket– A compression test will confirm whether or not the head gasket is leaking.
- Engine timing– The timing chain could have jumped, or there could be an issue with the crank or cam sensor.
- Burned Valve or Broken Valve Spring– A burned valve will reduce the compression rate and cause a misfire.
- Clogged Catalytic Converter– A clogged cat can increase backpressure and cause misfiring.
Bad Gas

Old gas can cause misfiring.
If your misfire started a minute or two after filling up, it could be that your Firebird has some bad gas. The same goes if it’s been sitting for over 90 days.
How to Fix P0300 in the Pontiac Firebird
P0300 will often be fixed by something obvious. When it’s not glaringly obvious what is wrong, a tune-up is a great place to start. Here’s a good order to approach fixing P0300 in the Pontiac Firebird.
- Check for other codes. Use them to eliminate as many of the causes listed above as you can.
- Check the wiring harness going to the coil packs. Verify that it isn’t burnt, frayed, or otherwise damaged. If it’s wintertime, look for signs of rodent damage.
- Pull a few random plugs. Replace them if needed.
- Test the coil packs.
- If your Firebird has plug wires. Run the engine in the dark and see if you see any spark “leaking”.
- Check for a vacuum leak.
- Test the fuel pressure.
- Do a compression test.
Q & A
Q: Is P0300 a serious concern?
A: P0300 is cause for concern, and left unfixed can get worse. Left ignored, a misfire will eventually get bad enough that your Firebird may not start.
Q: Can a bad catalytic converter cause P0300?
A: Yes. A clogged converter will increase backpressure. An engine is a pump. When there’s too much backpressure, air can’t quickly move through the combustion chambers and will misfire.
Q: How do you clear P0300?
A: You can use an OBD II scanner to clear P0300 in the Pontiac Firebird. You have to fix the root cause of P0300 in your car. Otherwise, when you clear the code, it’ll come right back.

