
The Chevy Silverado is a great truck that can last many miles with no issue. However, like any vehicle, it can face issues and malfunctions from time to time.
One such problem that can occur in the Silverado is the tendency to not shift gears properly. When this happens, the first thing you should do is check the transmission fluid.
There could be various reasons for the Chevy Silverado’s gear shifting issues, such as misaligned throttle position sensors, malfunctioning shift solenoids, or even general wear and tear related to higher mileage.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of these shifting problems is crucial for Silverado owners, as it helps them to diagnose the issue and seek the appropriate repair solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Checking the transmission fluid is the first step you should take in diagnosing a Chevy Silverado that won’t shift.
- Misaligned throttle position sensors and malfunctioning shift solenoids are possible causes.
- Diagnosing the issue and seeking proper repair can help ensure smooth operation.
- This issue usually requires a professional diagnosis.
Common Causes of Gear Shifting Problems
Transmission Fluid Issues

One common cause of gear shifting problems in a Chevy Silverado is issues with the transmission fluid. Transmission fluid plays a crucial role in the operation of the transmission, allowing gears to shift smoothly and providing proper lubrication to prevent wear.
Low or contaminated fluid can lead to poor shifting performance, hesitation, and even damage to the transmission. It is essential to regularly check the fluid levels and replace it as necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Faulty Transmission Solenoids
Faulty transmission solenoids are another possible cause of gear shifting issues in Chevy Silverados.
Transmission solenoids are responsible for controlling the flow of transmission fluid throughout the transmission system. When these solenoids aren’t functioning correctly, they can cause the transmission to not shift properly or at all. Replacing the faulty solenoids may resolve the problem.
Malfunctioning Transmission Control Module

The transmission control module (TCM) is responsible for managing the transmission’s operation, including shifting gears.
A malfunctioning TCM can cause several issues, such as not shifting correctly or not shifting at all. If the TCM is not functioning as it should, it may need to be replaced or reprogrammed.
Shift Linkage or Cable Problems
Finally, issues with the shift linkage or cables can also cause gear shifting problems in a Chevy Silverado. These components connect the gear shift lever to the transmission, allowing the driver to change gears manually.
Damage or wear to the linkage or cables can lead to difficulty shifting or even the inability to shift gears altogether. Inspecting and replacing the damaged parts of the shift linkage or cables may help to resolve gear shifting issues.
Symptoms of Chevy Silverado Shifting Issues
Delayed Gear Engagement
Delayed gear engagement is a common symptom of transmission problems in Chevy Silverados. It refers to a hesitation or delay when shifting gears or a reluctance to shift into certain gears.
This could be caused by various issues within the transmission, such as high temperatures or worn-out gears. You may notice that your truck takes longer than usual to shift from one gear to another, or that the engine revs higher than normal before the transmission finally shifts.
Shifting Without Warning
Another symptom of shifting issues in a Chevy Silverado is unexpected shifts occurring without any warning.
This can happen when the transmission quickly and suddenly shifts into a different gear, causing the driver to lose control or feel a jolt. This could be due to problems with the shift solenoids, the throttle position sensor, or other internal transmission components.
Difficulty Changing Gears
Chevy Silverado owners may also experience difficulty when attempting to change gears. This can manifest as a resistance or struggle to move the gear shifter, or even difficulty selecting the desired gear altogether.
Such issues can result from internal transmission damage, low transmission fluid, or an improperly adjusted throttle position sensor. Drivers with this symptom should seek a thorough diagnosis from a qualified mechanic to pinpoint the underlying cause and correct it.
Strange Noises When Shifting
Finally, strange noises accompanying gear shifts could be indicative of transmission problems in a Chevy Silverado.
You may hear grinding, humming, or whining sounds during shifts or when the transmission is attempting to engage a gear. These unusual noises could potentially indicate worn-out gears, damaged bearings, or other internal transmission components requiring repair or replacement.
Having a professional mechanic assess the situation is essential for determining the cause and the smart move.
Diagnosing Transmission Problems

When a Chevy Silverado encounters issues with shifting gears, it is essential to diagnose the problem accurately. To do so, consider using the following methods:
Visual Inspection
The first step in diagnosing transmission problems is a thorough visual inspection. Check the transmission fluid level and its condition, as low or contaminated fluid can cause hard shifts or slipping.
Inspect the wiring and connections to the transmission for signs of wear or damage, as corroded or loose connections can impair signal transmission.
Be sure to inspect the transmission linkage and bushings for wear, as worn or damaged components can cause the Silverado to struggle during gear changes.
Additionally, examine the throttle position sensor to ensure that it is functioning correctly and providing accurate data to the transmission control module (TCM).
Trouble Code Analysis

The next step is to analyze any trouble codes stored in the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system. These codes can provide valuable insight into potential issues with the transmission.
Common codes related to transmission problems include those related to shift solenoids, transmission control modules, and throttle position sensors.
To read the codes, use an OBD-II scanner to connect to the vehicle’s diagnostic port. Once the scanner has retrieved the relevant error codes, consult a repair manual or online resources specific to the Chevy Silverado to interpret the codes and determine the appropriate course of action.
Specialized Diagnostic Tools
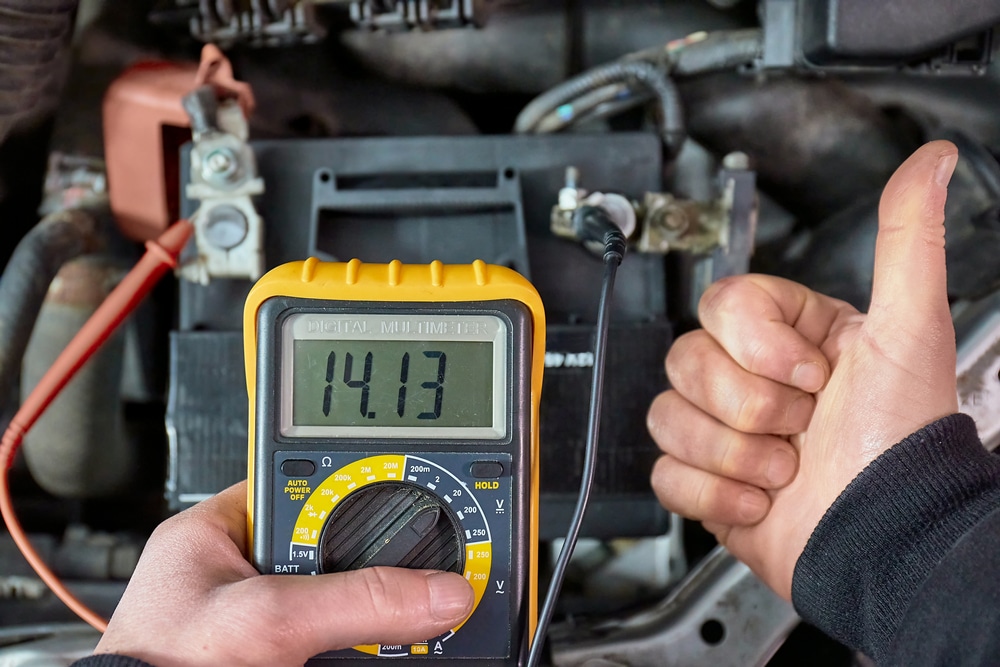

Some transmission problems may require specialized diagnostic tools to pinpoint the issue. One such tool is a pressure gauge designed to monitor transmission fluid pressure.
If the pressure is abnormal or erratic, it could indicate a problem with the transmission’s hydraulic system, such as a faulty valve body or internal seal.
Another valuable tool is a multimeter, which can be used to check the electrical components of the transmission system, including solenoids and sensors. With a multimeter, you can measure resistance, voltage, and current to ensure the components are functioning correctly and within the specified range.
Using a combination of visual inspection, trouble code analysis, and specialized diagnostic tools, you can accurately diagnose transmission problems in a Chevy Silverado and apply the necessary fixes to get it back on the road.
Solutions and Repair Procedures
Fluid Level and Quality Check
A crucial first step in addressing Chevy Silverado shifting issues is to check the fluid level and quality. This involves assessing the transmission fluid for an appropriate color, adequate level, and absence of debris.
Low or contaminated fluid can lead to erratic shifting and poor transmission performance. If the fluid appears dark or burnt, it is recommended to flush the system and replace it with fresh fluid.
Solenoid and Control Module Replacement
For automatic transmissions, solenoid issues or malfunctioning control modules can lead to shifting problems. One possible solution is to replace the faulty shift solenoid or the automatic transmission control module (TCM, PCM).
These components are responsible for informing the transmission when to shift gears, and their failure can directly affect gear-shifting performance. It’s important to diagnose and replace these parts if they are found to be faulty.
Adjusting or Fixing Linkage and Cables
In some cases, the linkage and cables responsible for transmitting the gearshift input may become improperly adjusted or damaged.
In these situations, it is essential to inspect the connections and adjust, repair, or replace any faulty or misaligned components. Properly aligning the linkage and cables can resolve problems with gear shifting and improve the overall transmission performance.
Maintenance Tips to Prevent Shifting Issues
Regular maintenance can help prevent shifting issues in a Chevy Silverado. Following a few simple steps will ensure the truck’s transmission and gears function smoothly.
Check the Transmission Fluid Regurarly
First, it is essential to check and maintain the transmission fluid levels. Low or dirty transmission fluid can cause gears to shift improperly.
It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the correct transmission fluid type and intervals for replacement. In most cases, this would involve checking the fluid level every 30,000 miles and changing it every 60,000 to 100,000 miles.
See your Chevy owner’s manual for the exact maintenance schedule.
Pay Attention to Changes
Another critical factor in preventing gear shifting issues is to pay attention to the truck’s performance. If your Silverado is displaying signs of gear hunting, stalling, or jerking while shifting, these might be early indications of a problem.
Tire Size and Alignment
In addition, proper tire balancing and alignment play a role in transmission performance. Larger or improperly balanced tires can cause stress on the transmission, leading to gear shifting issues.
It is crucial to keep the tires balanced, aligned, and inflated per manufacturer specifications to maintain optimal transmission functionality.
Some Silverado owners have experienced satisfactory results by adjusting the shifting points of the truck. This can be done with the help of a professional tuner who can reprogram the truck’s computer to shift gears at different RPMs. This may improve overall ride quality and put less stress on the vehicle.

